
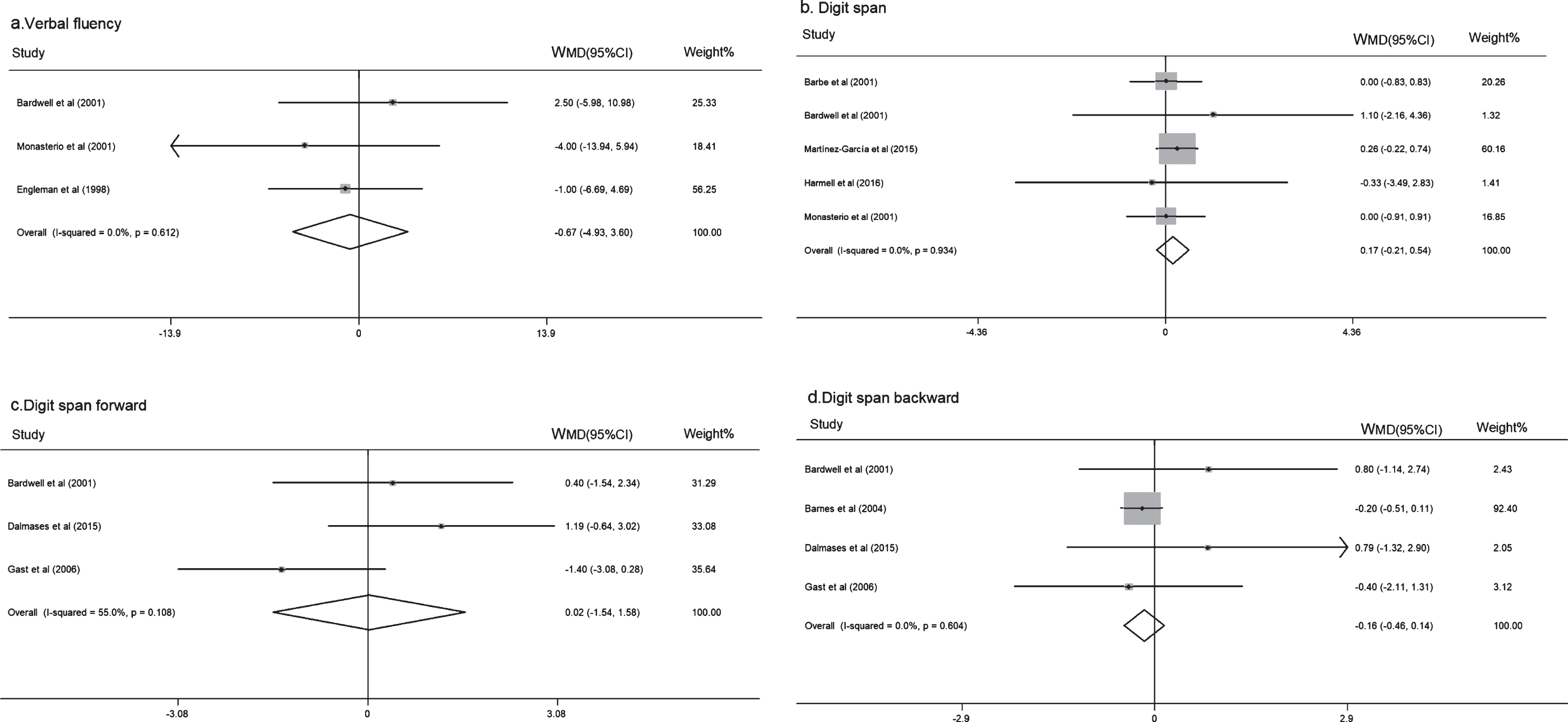
Consequently, the present study will also investigate whether the forward and backward digit span performances of patients with brain injury similarly or differentially correlate with and/or predict their attention and executive functioning performance. Each sub-scores of digit span test (forward, backward, and sequential) was coded separately for statistical analysis. The results support the notion that forward and backward digit span. However, research evidence suggests that forward digit span (immediately recalling digits in the same order) is representative of short-term memory functioning, whilst backward digit span (immediately recalling digits in reverse order) is representative of working memory capacity. In the first part, the subject listens to a sequence. Memory span is a common measure of working memory and short-term memory. The verbal span test (forward and backward digit span5) is an attention and memory task with 2 parts. The task is known as digit span when numbers are used. Items may include words, numbers, or letters. Using a regression analysis we will examine whether the digit span performance of patients correlates with and/or predicts their performance on neuropsychological measures of attention and executive functioning. In psychology and neuroscience, memory span is the longest list of items that a person can repeat back in correct order immediately after presentation on 50 of all trials. Although the format of the forward and backward Corsi block test are analogous to the forward and backward forms of the digit span task (which tests verbal memory span rather than visuo-spatial memory span), the backward Corsi block tapping test differs from the backwards digit span task in its relative difficulty. To achieve the study aims we will access an anonymous, pre-collected database containing the neuropsychological test scores of patients referred to and assessed in a specialist Neuropsychology service. These subtests reflect the empirical and educational tasks described throughout this chapter.The other six subtests address the visual-spatial sketchpad and. For the Backward Digit Span, the sequence had to be typed in reverse order. For the Forward Digit Span, the sequence had to be typed in as it was originally presented. Then, the final digit was removed and the participant had to type in the sequence. Counting Recall, and Backward Digit Recall tasks. Each digit was presented at the center of the screen for 1 s. Furthermore, the proposed investigations have implications for working memory training, they will allow us to investigate whether specifically training the working memory span of patients with brain injury could facilitate improvements in other high order cognitions, transfer effects that are proposed in the working memory training literature. The Working Memory Test Battery for Children (WMTB-C) assesses working memory in children aged 5 to 15 (Pickering & Gathercole, 2001). attention and executive functioning, in a sample of patients who have sustained a brain injury. The present study aims to investigate whether digit span performance (number of digits immediately recalled) is associated with performance on neuropsychological measures of high order cognitions i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
